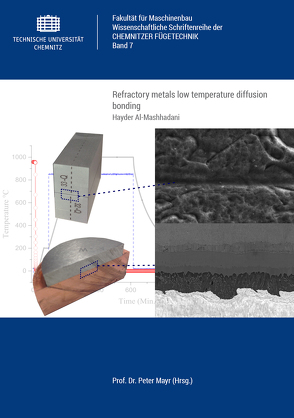
Refractory metals low temperature diffusion bonding
Hayder I. Saleh Al-Mashhadani
In this dissertation, the minimization of the diffusion bonding
temperature during refractory metals’ diffusion bonding process was
studied. Two pure refractory metals were used in this study:
molybdenum and tungsten. The influence on the joint quality of
molybdenum structural conditions, as well as molybdenum surface
conditions, was examined. Moreover, diffusion bonding of tungsten to
Oxygen Free Electrical copper and copper alloy (CuCr1Zr), without
using an interlayer but instead using different bonding parameters, was
evaluated. Diffusion bonding of tungsten to Oxygen Free Electrical
copper and to CuCr1Zr alloy using titanium and nickel together as
intermediate layers was also investigated, as well as the diffusion bonding of tungsten to Oxygen Free Electrical copper and to CuCr1Zr
alloy using only nickel as an intermediate layer.
The resulting joints were evaluated using optical microscopy,
SEM, hardness, shear, and tensile tests. The residual stresses, as well
as the deformation, that are generated due to the diffusion bonding
process were evaluated through a FEM simulation using the software
ANSYS.
For pure molybdenum joints, successful results in minimizing
bonding temperature were obtained. In tungsten to Oxygen Free
Electrical copper and to CuCr1Zr alloy joints contrasting results were
achieved.